Introduction
The advent of large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4, Gemini, Llama, etc., is transforming natural language processing with significant implications for healthcare. A comprehensive study published on arXiv investigates the diagnostic accuracy of LLMs in recognizing symptoms of common health conditions, evaluating their potential to enhance accessibility and efficiency in digital diagnostics. By exploring their capabilities and limitations, the research sheds light on the future of AI for doctors including providing critical insights into the integration of LLMs into modern healthcare and their role in shaping the future of medicine.
We have carefully examined the study and highlighted its most impactful insights, ensuring they are presented in a clear and easily digestible format.
Methodology
The models used, i.e., GPT-4, Gemini, and GPT-3.5, were chosen to assess the diagnostic precision of LLMs.
Datasets used: The dataset chosen was of common, everyday ailments—like seasonal allergies, the common cold, and food-related issues—sourced from reputable medical organizations (CDC, WHO, Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, and Johns Hopkins Hospital).
Prompting strategy: Prompts were carefully designed by presenting the symptoms and asking for disease predictions with confidence scores, ensuring consistency in evaluation.
Comparison: A detailed symptom-disease dataset was formed, and manual verification was conducted to ensure accurate and reliable disease predictions. The models were scored across three parameters: Precision, Recall, and F1 score (a measure of overall diagnostic performance).
Results
The study highlights the impressive diagnostic capabilities of LLMs, with GPT-4 emerging as the leader, demonstrating its ability to map symptoms to diagnoses and handle complex medical language accurately. GPT-3.5 also displayed strong performance, balancing precision and recall effectively, making it a reliable tool in scenarios where cutting-edge models may not be necessary. Though generating fewer predictions, Gemini excelled in high-confidence precision, making it particularly suitable for critical diagnostic tasks requiring minimal error.
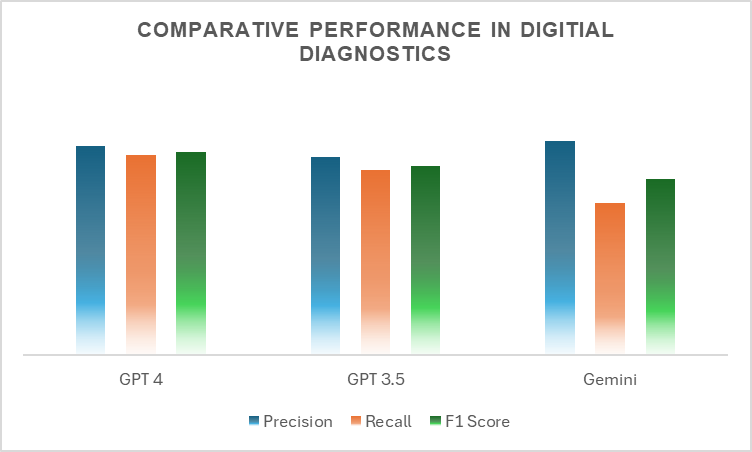
Fig: The figure highlights the performance of the LLMs across different metrics for an overall evaluation
Why this Matters for the Future of AI for Doctors
The results of this study are particularly interesting as they highlight the strengths of LLMs in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and reliability. The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into medical practice has the potential to revolutionize doctor-patient interactions, transforming the diagnostic process and paving the way for more precise and efficient healthcare delivery.
Benefits to the medical community
Doctors: LLMs can enhance the speed and quality of initial medical consultations, enabling faster patient assessments and reducing the burden on doctors.
Hospitals: LLMs can help clinics and hospitals streamline patient flow by providing quick preliminary diagnoses, prioritizing urgent cases, and reducing wait times.
Conclusion
Incorporating LLMs into healthcare holds great promise for enhancing diagnosis and patient care. Platforms like Dx, an AI search engine for healthcare professionals, showcase the value of AI for doctors for more accurate diagnosis by providing reliable insights and augmenting clinical decision-making. With regular validation and careful planning, LLMs can complement human expertise and improve patient outcomes.
Read the full story on arXiv. Also, discover Dx’s power with its specialized medical diagnostics module! Explore it here and share your feedback to help us improve it.
Interested in how AI is revolutionizing clinical diagnosis? Dive deeper by reading our article, “Transforming Cancer Diagnosis with the Power of AI”
