Introduction
Diagnosing gastrointestinal (GI) cancers has long been challenging due to complex symptoms and risks of misclassification, often delaying accurate clinical diagnosis and treatment. While traditional methods like imaging and endoscopy are valuable, they can fall short in providing quick precision. According to a recent study published on arXiv, large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT-3.5 Turbo, offer a promising solution by efficiently processing complex medical queries and delivering accurate, context-specific information, helping clinicians improve diagnosis and patient care.
We have thoroughly analyzed the research to distill its essential points, presenting them in a simplified and accessible manner for your convenience.
Methodology
The model used: GPT 3.5 Turbo model in zero-shot mode at temperature 0.7 was utilized.
Datasets used: 30 queries related to GI cancer were used for training the model, and 50 queries were used to test its performance.
Prompting strategy: Three types of prompts were designed to generate output for the question-answering task:
- Detailed prompt – A prompt that instructs the model to focus on the main ideas relevant to the given query.
- Direct query – In this prompt, the query was passed directly without any additional instructions, relying on the default behavior of the LLM to respond accurately.
- Summarization prompt – This prompt guided the model in generating concise, focused responses summarizing the essential information.
Comparison: The evaluation of the generated answers was assessed across two metrics:
- A1: Assesses how well the entities in the model’s response match those in the reference answer, focusing on content accuracy.
- A2: Evaluates the clarity and linguistic quality of the model’s response compared to the reference answer.
Results
The results show that the model’s performance improved over three test runs:
- For the A1 metric (accuracy of entities), scores increased from 0.354 to 0.546, showing better alignment between the model’s answers and the reference’s answers.
- For the A2 metric (linguistic quality), scores rose from 0.622 to 0.881, indicating improvements in the clarity and meaningfulness of the responses.
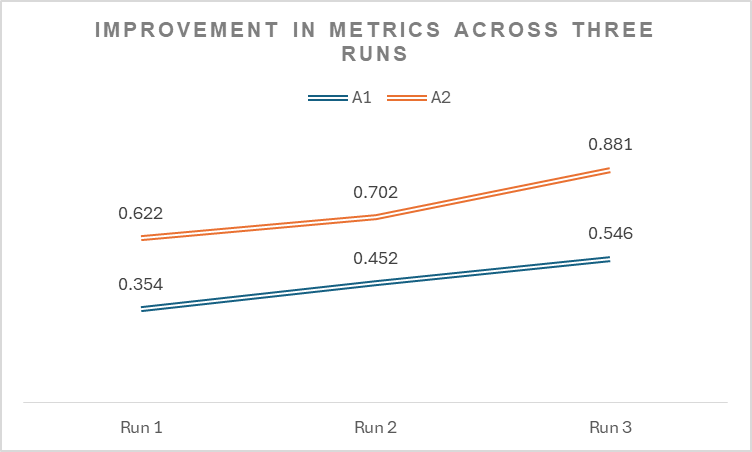
Fig: Values for evaluation metrics – A1 and A2 across three runs
These upward trends highlight the effectiveness of refining prompts and improving the system’s ability to handle cancer-related queries accurately and clearly.
How This Advances Accuracy in Clinical Diagnosis
The results showcase how advanced Large Language Models (LLMs), like GPT-3.5 Turbo, can revolutionize clinical diagnosis (particularly GI cancer) by providing precise, context-aware answers to complex queries. It marks a transformative step in oncology, overcoming traditional diagnostic challenges to improve accuracy and patient outcomes.
Benefits to the medical community
Oncologists – LLMs assist oncologists in clinical diagnosis by providing precise, context-aware answers to complex queries, enabling faster and more accurate differentiation of cancer types like GI cancers.
General practitioners – LLMs can help general practitioners by providing quick, reliable answers to complex cancer-related queries, aiding in early detection, referral decisions, and better patient education.
Conclusion
LLMs hold transformative potential in cancer detection by providing accurate, timely insights to support complex diagnoses such as GI cancers. Their ability to generalize across topics and adapt dynamically makes them invaluable for improving clinical decision-making. Platforms like Dx, AI search engines designed for healthcare professionals, further enhance this potential by offering streamlined access to critical information, empowering doctors to tackle challenging cases more effectively.
Read the full story on arXiv. Also, explore Dx’s potential with its specialized diagnosis module, designed to assist in accurate and timely medical diagnoses! Try it now and share your feedback to help us make it even better.